Product Overview:
Huawei ATN950B designed for 2G/3G/LTE, VLL (Virtual leased line) and integrated services bearing, ATN 950B is a comprehensive device with 10GE ports. The
compact design with 300mm depth and 2U height makes it occupy less space and satisfy all kind demands of machine room. ATN 950B
has large capacity of 56G and 6 flexible slots. The main control panel and power panel support redundancy, which can ensure the flexibility
and reliable of services. With the faith of Huawei ‘Any Media’, ATN950B has functions of multi-service access, clock transmit in any medium,
high precision frequency and time synchronism. Besides, it provides multiple access port, such as copper cable, fiber-optical and so on. It
can be co-cabinet with BTS BBU, which can save precious site resource and reduce the Capex of carrier.
Product Appearance:

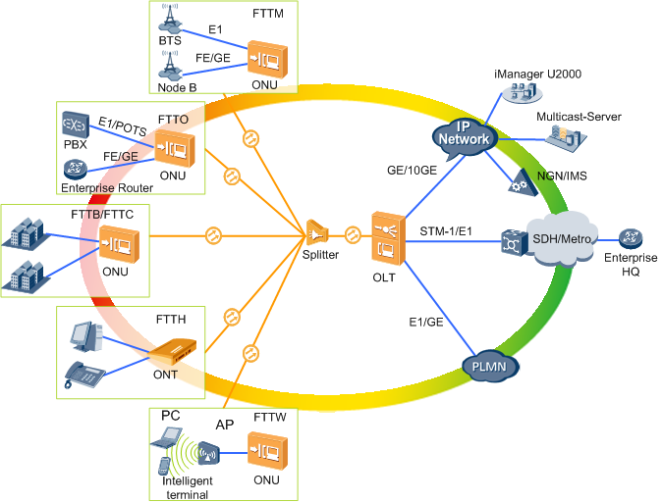
Network Position:
Designed for 2G/3G/LTE, VLL (Virtual leased line) and integrated services bearing, ATN 950B is a comprehensive device with 10GE ports. The
compact design with 300mm depth and 2U height makes it occupy less space and satisfy all kind demands of machine room. ATN 950B
has large capacity of 56G and 6 flexible slots. The main control panel and power panel support redundancy, which can ensure the flexibility
and reliable of services. With the faith of Huawei ‘Any Media’, ATN950B has functions of multi-service access, clock transmit in any medium,
high precision frequency and time synchronism. Besides, it provides multiple access port, such as copper cable, fiber-optical and so on. It
can be co-cabinet with BTS BBU, which can save precious site resource and reduce the Capex of carrier.
Product Features:
Compact 10GE Redundancy Platform: Only 2U height, coordinating with multiple security functions, ATN 950B has high reliability
with the main control panel redundancy, cross board redundancy and power panel redundancy.
Any Media Access: Multiple service access interfaces such as 10GE/GE/FE, Cpos, Smart E1 are supplied, so ATN 950B can totally meet
the demands of services and scenarios, boosting the unification of multiple networks at the last mile.
Large Capacity, All Services Borne: ATN 950B has eight 10GE ports, two 10GE ports of single slot which is better to satisfy the customer’s
service access demand. ATN 950B supports service comprehensive bearer of 2G/3G/LTE and VLL (Virtual leased line). As pre-AGG, and with
large capacity of 56G and FIB of 128K, ATN 950B can be applied in scenarios of 10GE rings, ring with chain and pre-aggregate node.
Big Buffer Design, Against Congestion Effectively: With the design of big buffer, ATN 950B series can against network traffic burst
effectively and promote customer experience.
Plug-and-Play, Replace-and-Play, High Efficiency Deployment: One time site visit and remote plug and play configuration can realize
services fast provisioning to 5 minutes. With the design of Built-in test packet generator (compliant with RFC2544/Y.1564), it is tester
free for the service deployment
Perfect Clock synchronization Solution: ATN 950B series supports IEEE1588v2 OC, BC and TC all mode, 1588 ACR, Synchronous
Ethernet, Adaptive clock recovery which perfectly solves the problems of high precision clock synchronization and in-buliding clock
coverage of mobile packet bearer network. ATN 950B series fulfills the clock synchronization requirement of LTE evolution in long run
and reduces investment on GPS and BITS.
Hardware NQA&OAM, Reliable Performance Statistics: ATN 950B series has the hardware-OAM capability. 3.3ms packet interval
ensures the fault be detected as fast as possible and services be switched within 50ms. It supports multiple OAM protocols (Y.1731,
Y.1564, BFD over everything, TWAMP and RFC2544 etc.). And, via collecting and detecting real-time services performances, the quality
status of the whole network is open-and-shut.
SDN-Based Software Architecture, Simplified O&M: Based on SDN software architecture, faced application, ATN 950B supplies
standard north API and south API to realize new service rapid innovation. The separation of controlling plane and forwarding plane
makes the disperse devices unified managed and service deployment decoupled from forwarding plan.